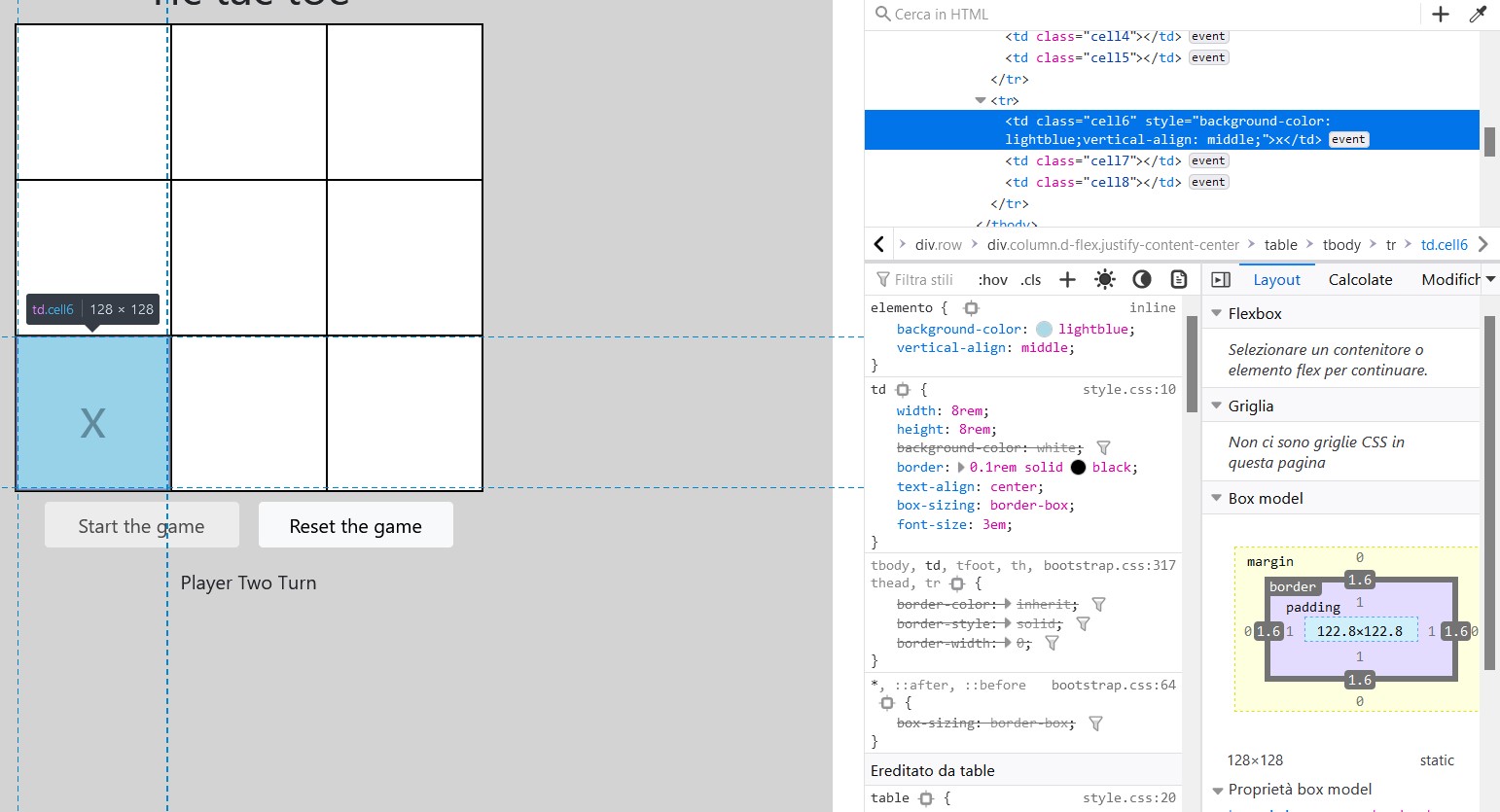
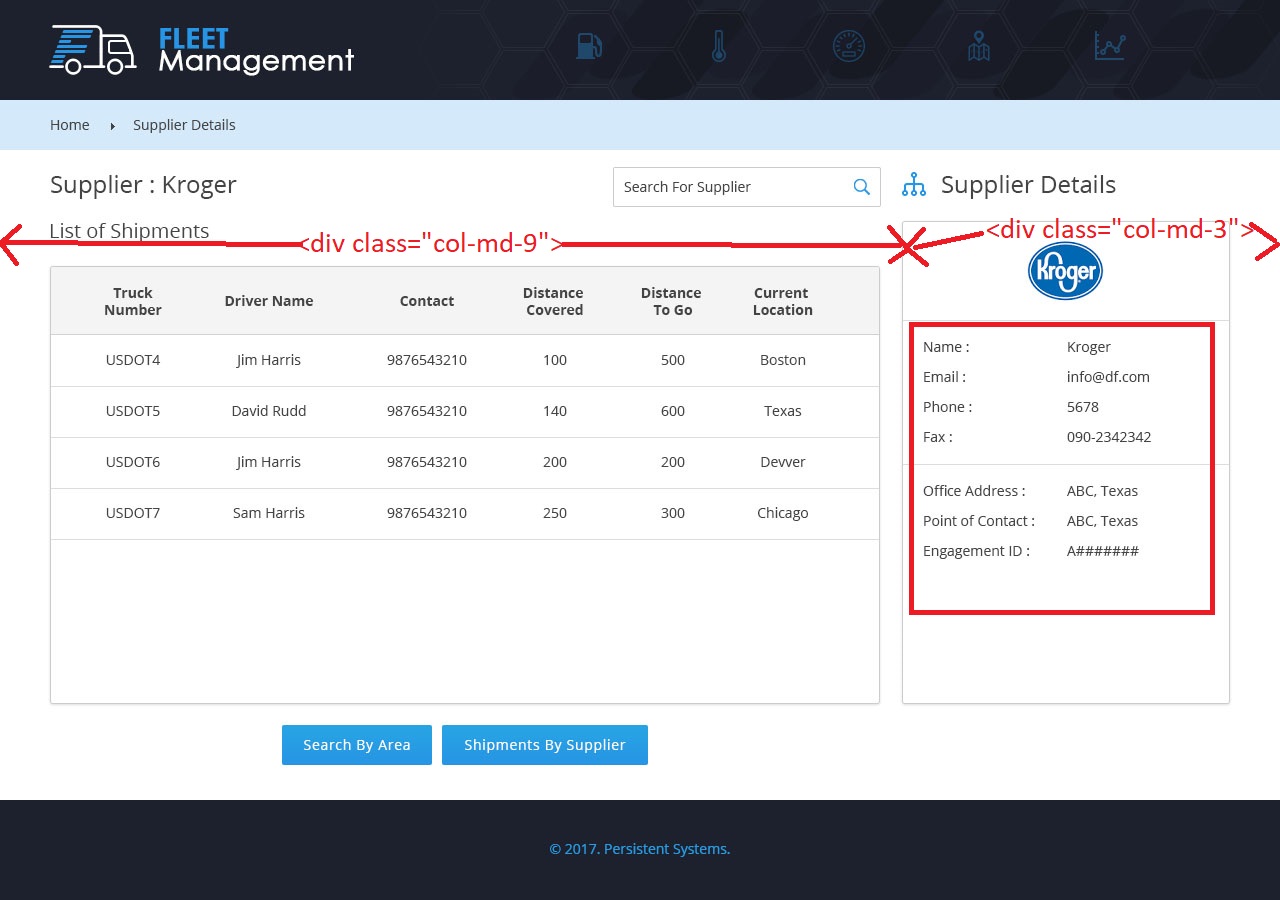
|
Panoramic view of the west bank of Nigeen Lake in Srinagar, India, with the distant Middle Himalayan Pir Panjal mountain range in the background. The city, situated on the banks of the Jhelum river and several lakes in the Himalayan Kashmir Valley, is the summer capital of Jammu and Kashmir and the northernmost million-plus city of India.
|