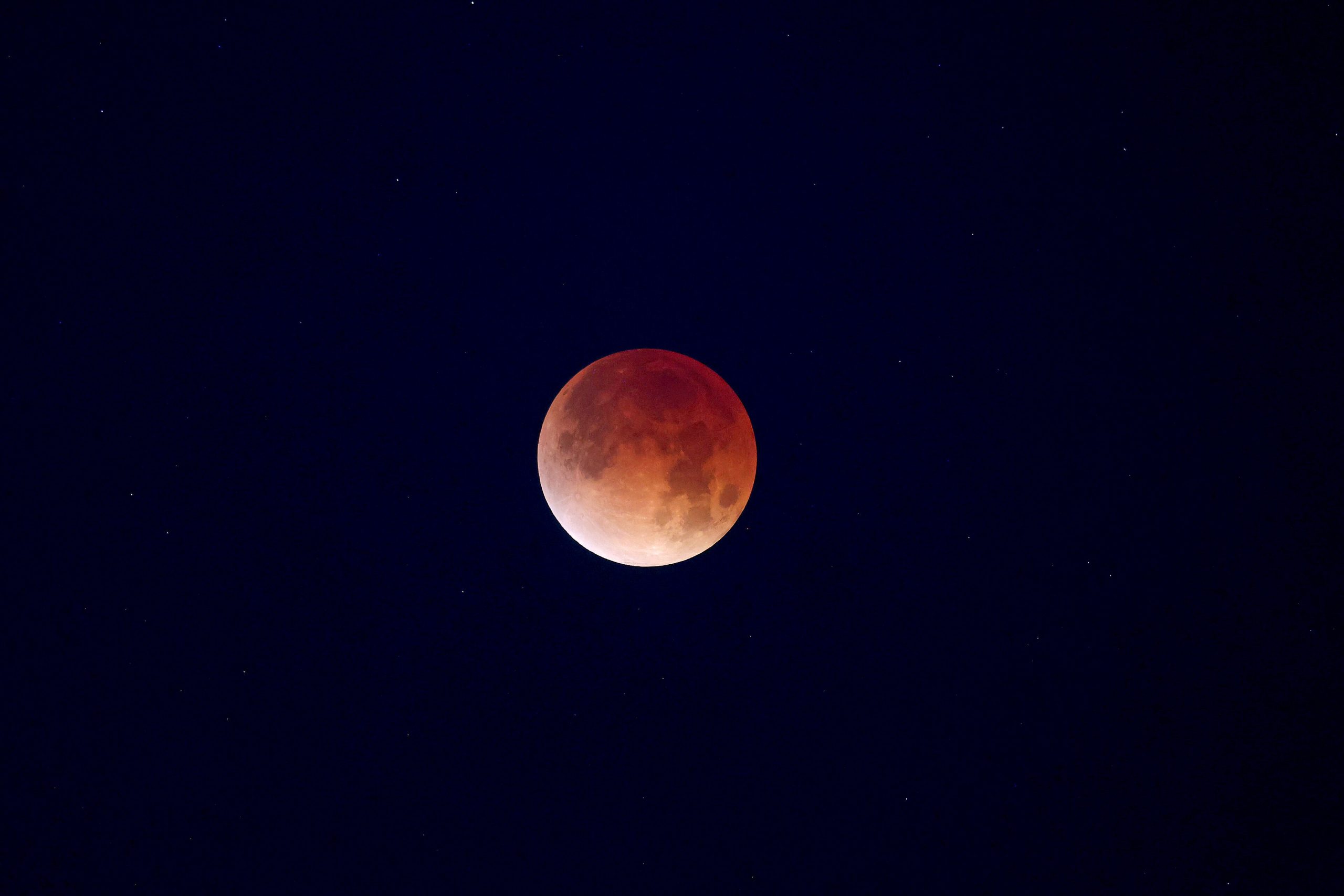





A total lunar eclipse rises over New Orleans, home of NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility, in the early morning hours of Tuesday, March 3. A lunar eclipse occurs when Earth passes directly between the Sun and Moon, casting a huge shadow across the Moon’s surface. The Moon appears dark red or orange as the Sun’s light filters through Earth’s atmosphere.
Read More
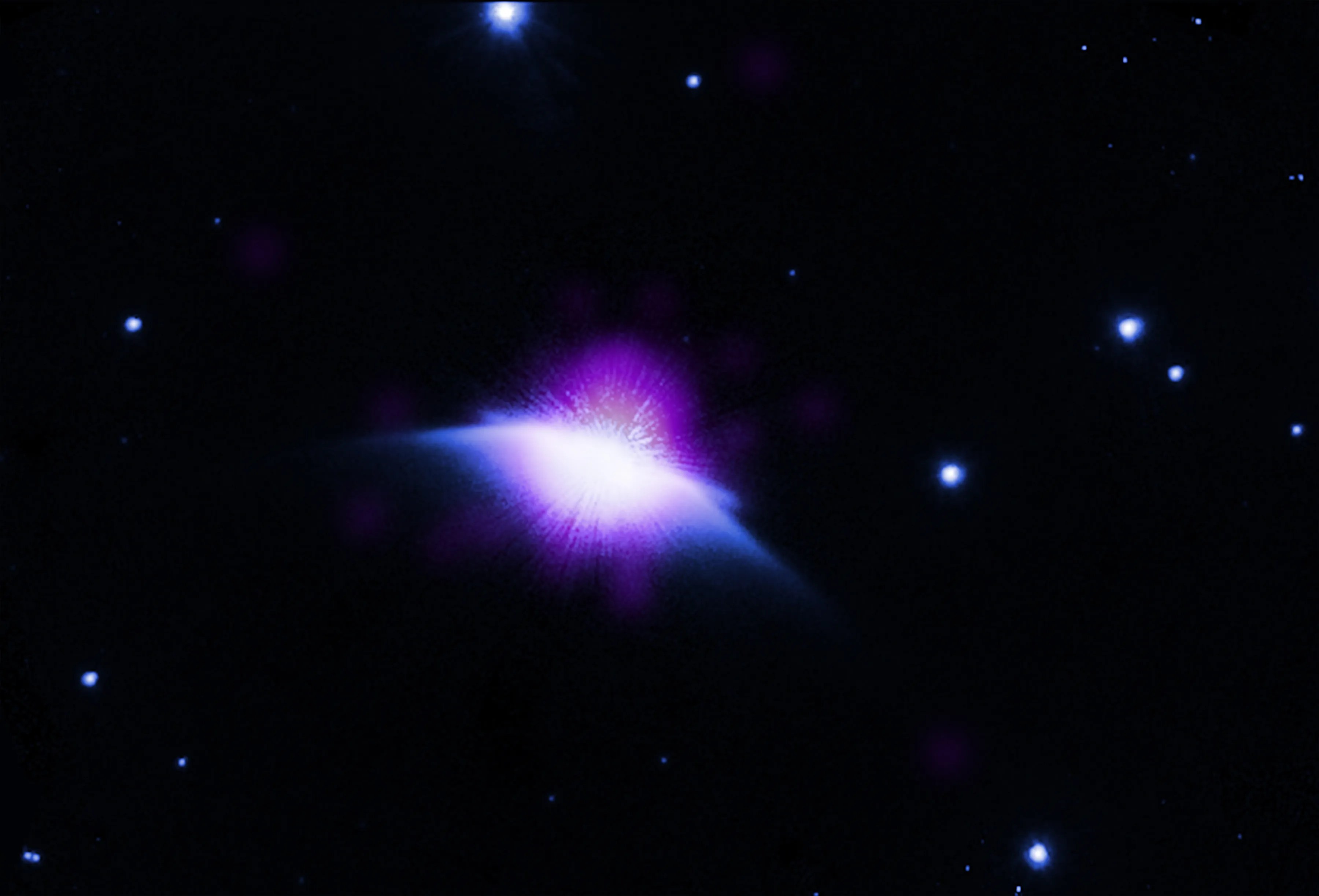

For the first time, a much younger version of the Sun has been caught red-handed blowing bubbles in the galaxy, by astronomers using NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory.
Read More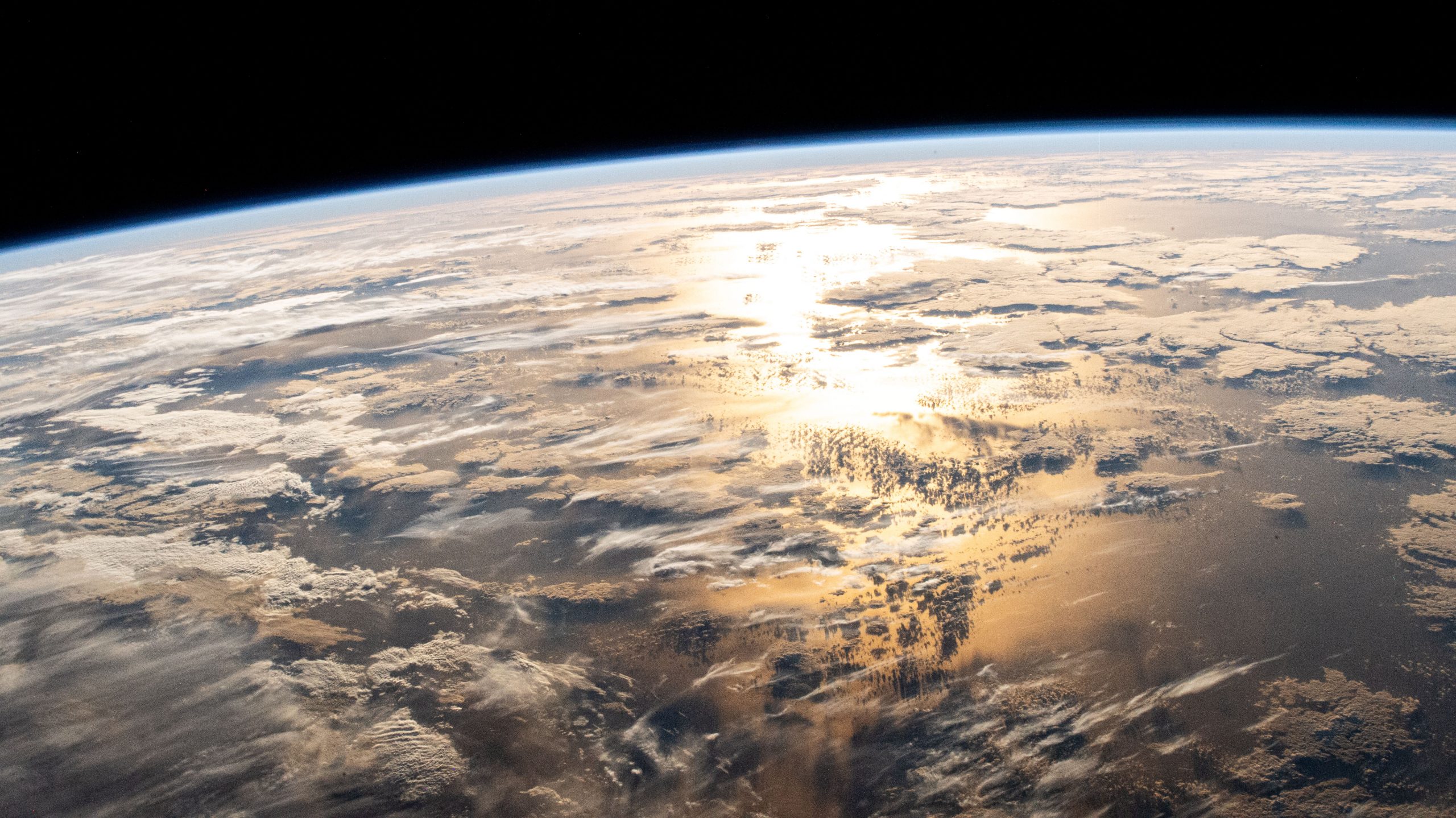

The sun’s glint beams off a partly cloudy Atlantic Ocean just after sunrise as the International Space Station orbited 263 miles above.
Read More
The Carbothermal Reduction Demonstration (CaRD) project aims to demonstrate the carbothermal reduction of lunar regolith to produce oxygen on the Moon’s South Pole. For this test, the team integrated the solar concentrator, mirrors, and software and confirmed the production of carbon monoxide.
Read More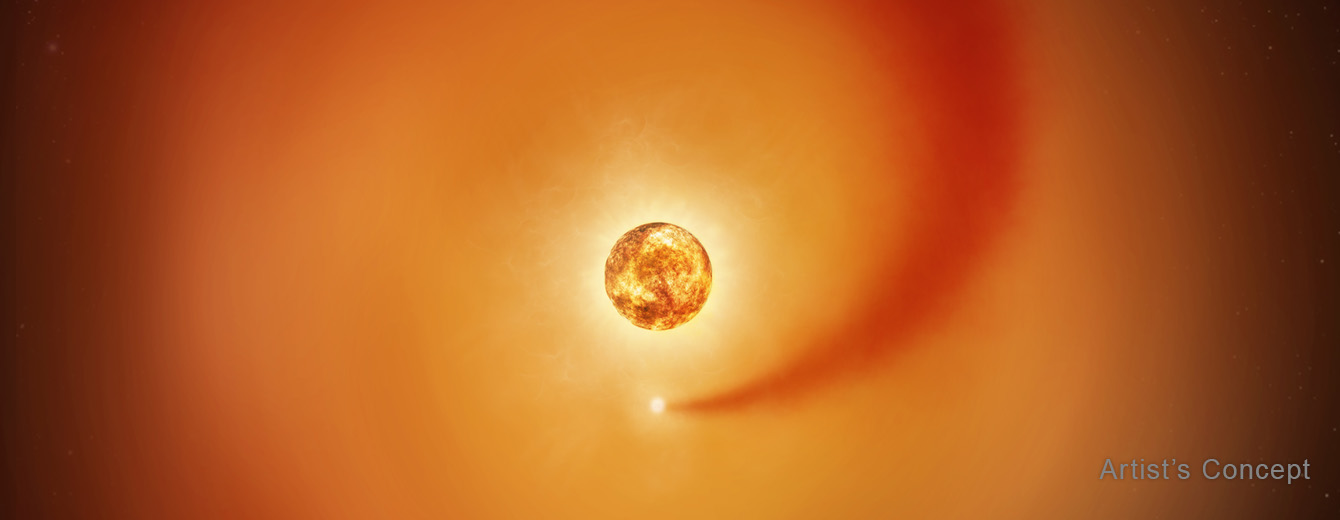
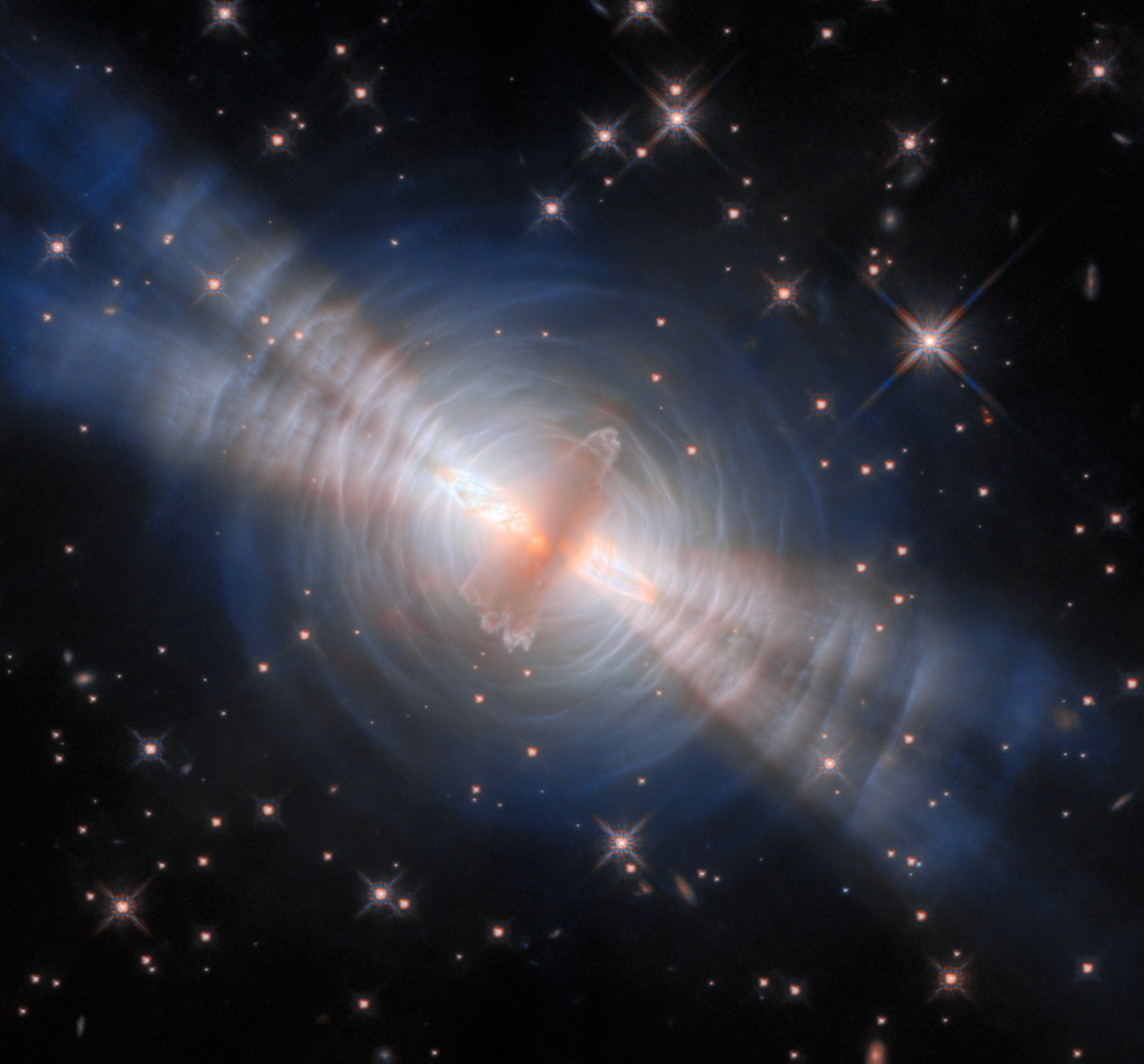

NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope reveals the clearest view yet of the Egg Nebula. This structure of gas and dust was created by a dying, Sun-like star. These newest observations were taken with Hubble’s Wide Field Camera 3.
Read More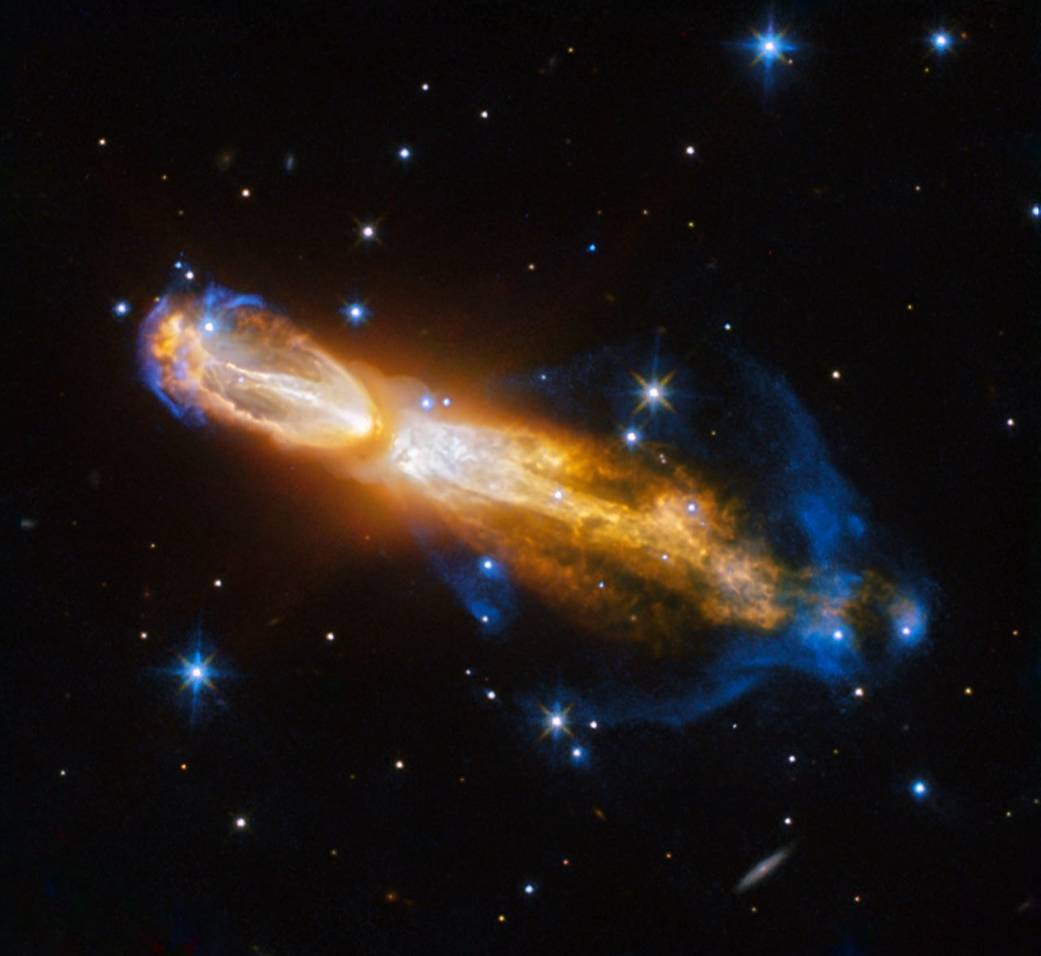

The Calabash Nebula, pictured here — which has the technical name OH 231.8+04.2 — is a spectacular example of the death of a low-mass star like the Sun. This image taken by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope shows the star going through a rapid transformation from a red giant to a planetary nebula, during which it blows its outer layers of gas and dust out into the surrounding space. The recently ejected material is spat out in opposite directions with immense speed — the gas shown in yellow is moving close to a million kilometres an hour. Astronomers rarely capture a star in this phase of its evolution because it occurs within the blink of an eye — in astronomical terms. Over the next thousand years the nebula is expected to evolve into a fully fledged planetary nebula. The nebula is also known as the Rotten Egg Nebula because it contains a lot of sulphur, an element that, when combined with other elements, smells like a rotten egg — but luckily, it resides over 5000 light-years away in the constellation of Puppis (The Poop deck).
Read More

| Picture of the day |
|---|

|
|
A beach chair on the beach of Juliusruh is illuminated by the rising morning sun.
|


A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA’s IMAP (Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe), the agency’s Carruthers Geocorona Observatory, and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Space Weather Follow On–Lagrange 1 (SWFO-L1) spacecraft lifts off from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 7:30 a.m. EDT Wednesday, Sept. 24, 2025. The missions will each focus on different effects of the solar wind — the continuous stream of particles emitted by the Sun — and space weather — the changing conditions in space driven by the Sun — from their origins at the Sun to their farthest reaches billions of miles away at the edge of our solar system.
Read More
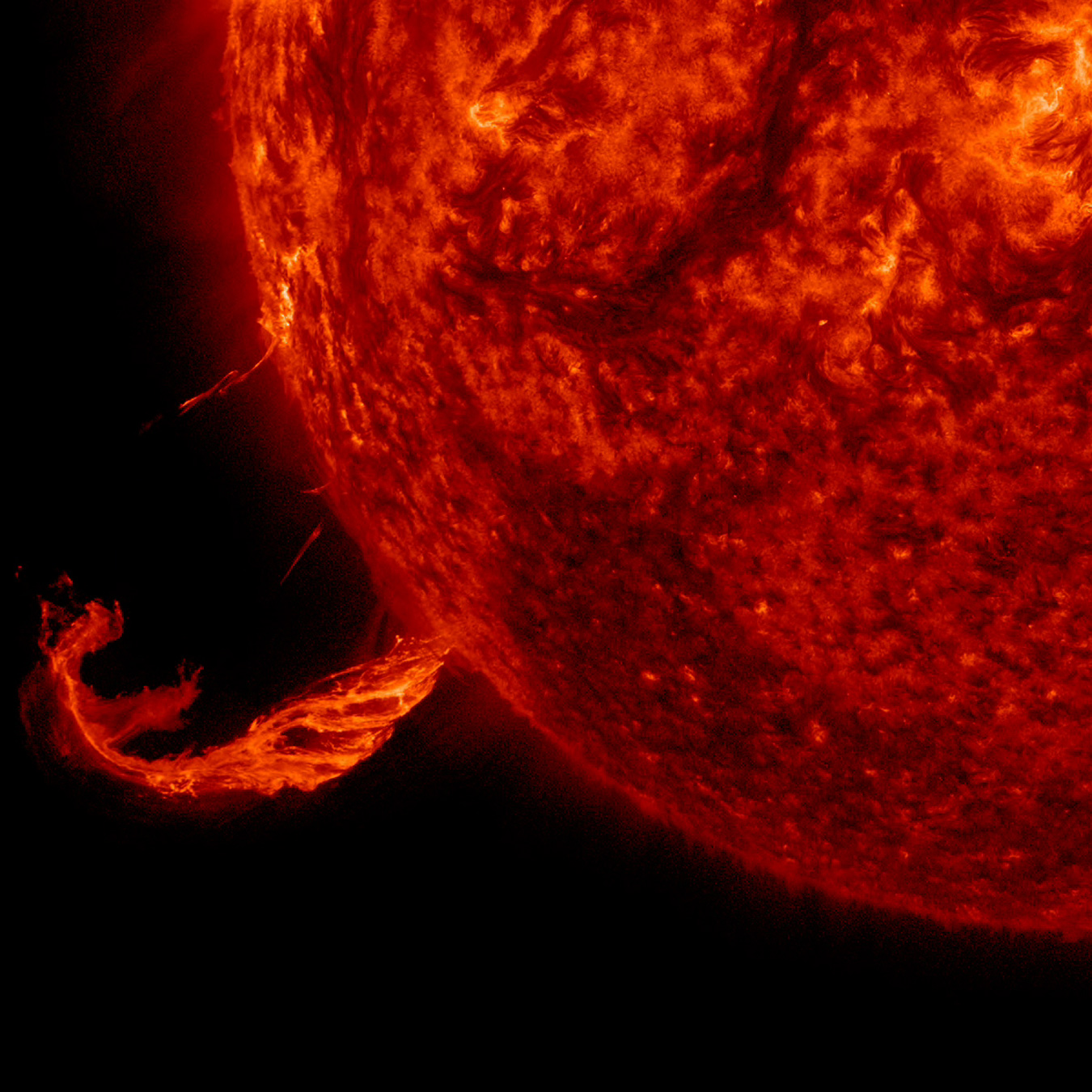

The Sun blew out a coronal mass ejection along with part of a solar filament over a three-hour period on Feb. 24, 2015. While some of the strands fell back into the Sun, a substantial part raced into space in a bright cloud of particles (as observed by the NASA-ESA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory spacecraft). Because this occurred way over near the edge of the Sun, it was unlikely to have any effect on Earth.
Read More

On May 19th, 2005, NASA’s Mars Exploration Rover Spirit captured this stunning view as the Sun sank below the rim of Gusev crater on Mars. This panoramic camera mosaic was taken around 6:07 in the evening of the rover’s 489th Martian day, or sol.
Read More

Webb has found crystalline water ice in a debris disk around a young, Sun-like star called HD 181327. Based on its presence in our own solar system, scientists have expected to see it in other star systems — but haven’t had sensitive enough instruments to provide definitive proof until now.
Read More

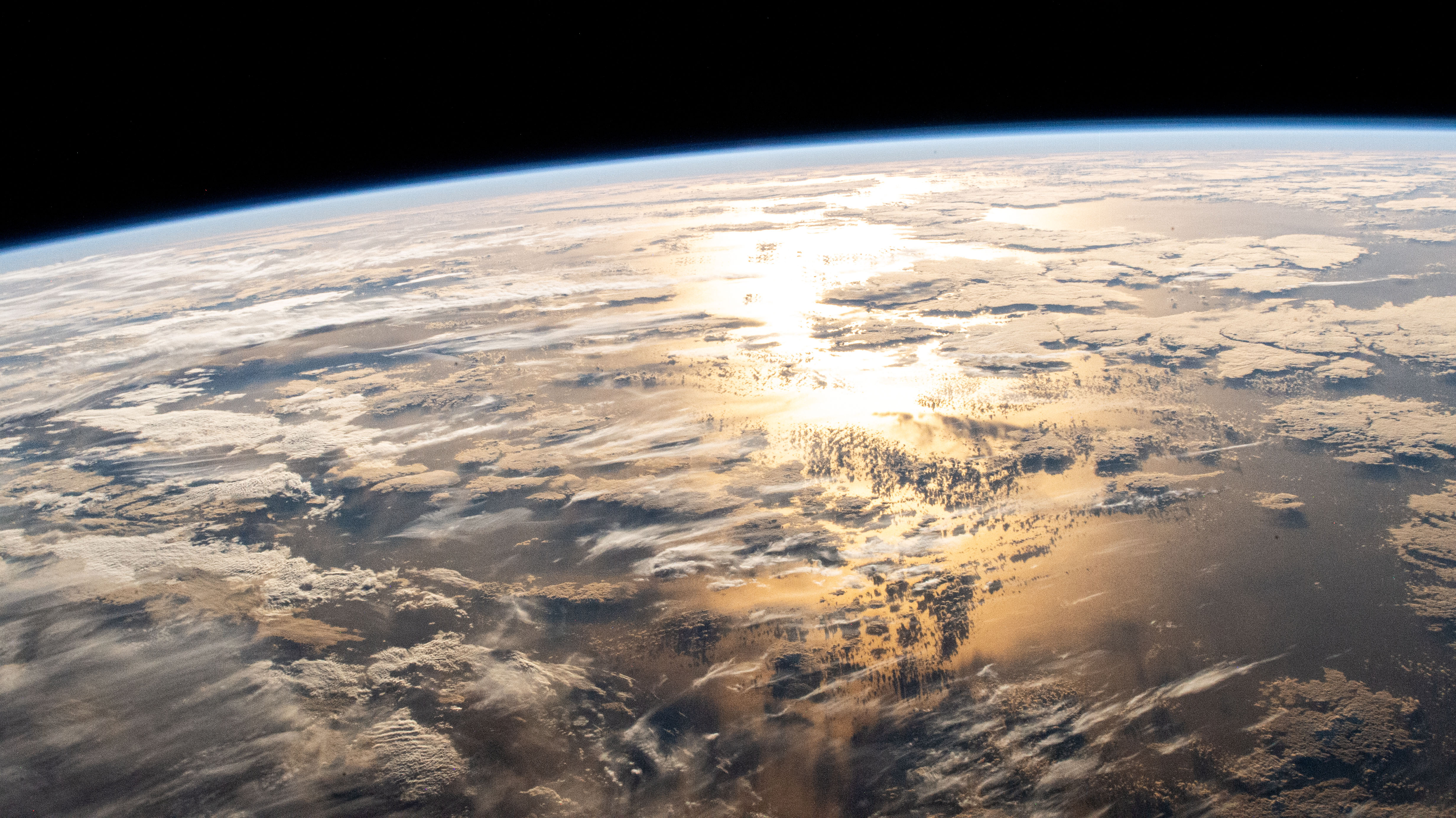
The sun’s glint beams off a partly cloudy Atlantic Ocean just after sunrise as the International Space Station orbited 263 miles above on March 5, 2025.
Read More

In about 5 billion years, our Sun will run out of fuel and expand, possibly engulfing Earth. These end stages of a star’s life can be utterly beautiful – as is the case with this planetary nebula called the Helix Nebula. Astronomers study these objects by looking at all kinds of light. This images show X-rays from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory (magenta), optical light data from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope (orange, light blue), infrared data from the European Southern Observatory VISTA telescope (gold, dark blue), and ultraviolet data from GALEX (purple) of the Helix Nebula.
Read More

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with the company’s Dragon spacecraft on top is seen during sunrise on the launch pad at Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, March 11, 2025, ahead of the agency’s SpaceX Crew-10 launch. Crew-10 is the 10th crew rotation mission with SpaceX to the International Space Station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Liftoff is targeted for 7:48 p.m. EDT on Wednesday, March 12, 2025.
Read More