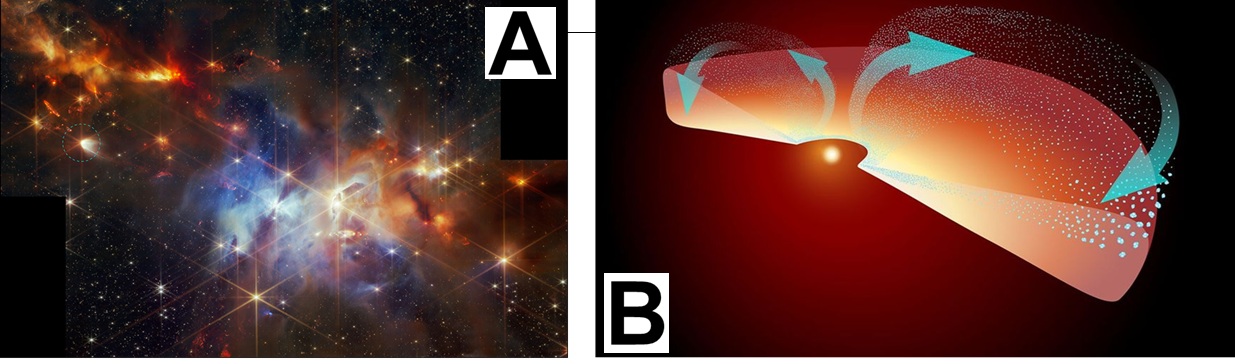
<div class="media_block"><img src="https://www.nasa.gov/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/stsci-01keswn3g28kzcqpz2ghhdkac3-e1f0ce.png"></div>NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope’s 2024 NIRCam image shows protostar EC 53 circled. Researchers using new data from Webb’s MIRI proved that crystalline silicates form in the hottest part of the disk of gas and dust surrounding the star — and may be shot to the system’s edges.

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope’s 2024 NIRCam image shows protostar EC 53 circled. Researchers using new data from Webb’s MIRI proved that crystalline silicates form in the hottest part of the disk of gas and dust surrounding the star — and may be shot to the system’s edges.
Source: https://www.nasa.gov/image-detail/stsci-01keswn3g28kzcqpz2ghhdkac3-e1f0ce/